Step 2: Adding a Logic Node
After retrieving data with a Data Source Node, the Logic Node is where you perform calculations, transformations, filtering, grouping, or any other custom manipulation of that data.
Decode makes this powerful by allowing you to describe the logic you need in plain English using an AI analyst. The AI then generates code to implement your logic and runs the logic behind the scenes.
Adding the Node
-
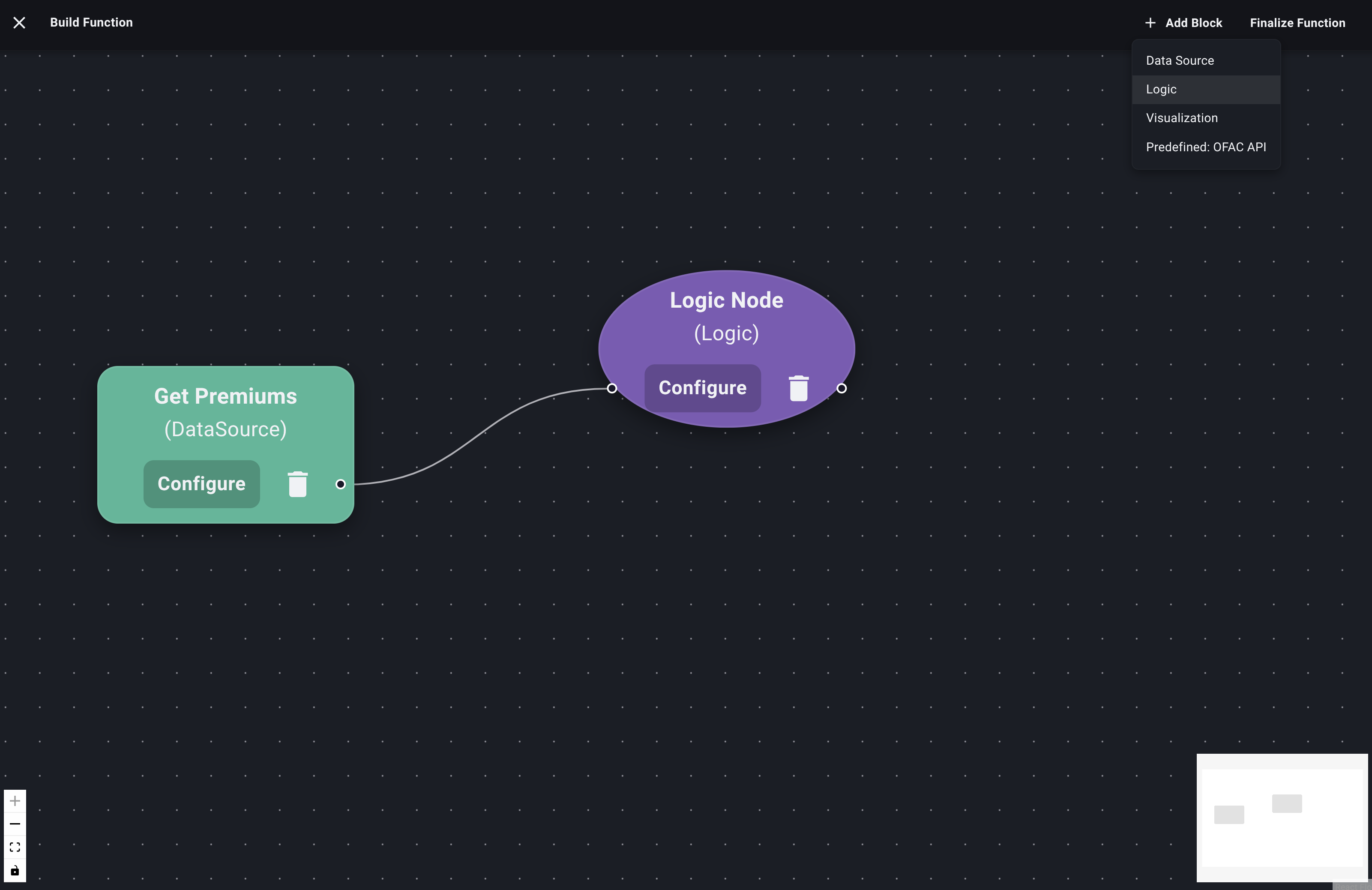
Open the "Add Block" Menu: In the Function Builder Dialog, click "Add Block".
-
Select "Logic": Choose "Logic" from the menu.
-
A new Logic node will appear on the canvas.
Add Logic Node -
Connect Nodes: You need to connect the output handle (usually on the right) of your Data Source Node to the input handle (usually on the left) of the new Logic Node. Click and drag from one handle to the other.
- Important: You generally must connect an input (like a Data Source Node) before you can configure the Logic Node.
Configuring the Logic Node (Interacting with AI)
-
Open Configuration: Click the "Configure" button on the Logic Node.
-
The Logic Block Configuration panel or dialog will appear. This interface is primarily a chat window.
Configure Logic Node -
Name (Optional but Recommended): Give this logic step a descriptive name (e.g., "Calculate Loss Ratio", "Filter California Policies", "Group by Wholesaler").
-
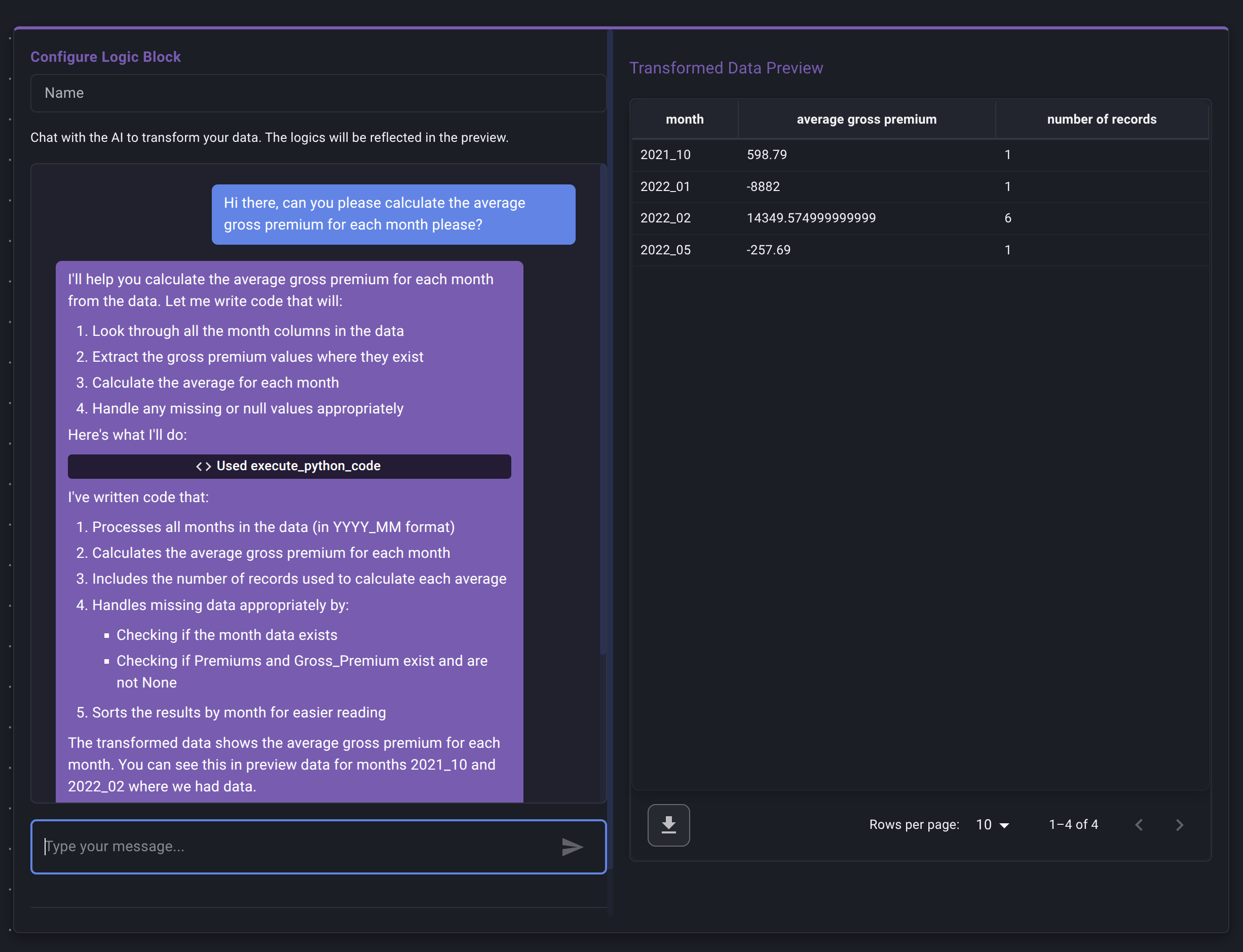
Instruct the AI: In the chat input box at the bottom, type instructions describing the transformation or calculation you want to perform on the data coming from the connected input node(s). Be clear and specific.
Examples:
- "Calculate a new column called 'Net Premium' by subtracting the 'Commission Amount' column from the 'Gross Premium' column."
- "Filter the data to only include rows where the 'Policy State' column is equal to 'CA'."
- "Group the data by the 'Wholesaler Name' column and calculate the sum of 'Net Premium' for each wholesaler. Call the summed column 'Total Net Premium'."
- "Show me all the policies that missed a premium payment inside of their contract window."
-
Send Message: Press Enter or click the Send button.
-
AI Processing: Decode's AI assistant will:
- Interpret your request.
- If the AI needs any clarity or further specification, it will ask follow up questions.
- Generate Python code to perform the requested operation.
- Run this code on a sample of the input data.
- Respond in the chat, confirming its understanding or showing the sample results.
-
Review AI Response & Preview:
- Read the AI's text response.
- Crucially, look for a Preview Table displayed within or alongside the chat. This shows the result of the AI's generated code applied to the sample data.
- Verify the Preview: Does the output table look correct?
Chat with the AI -
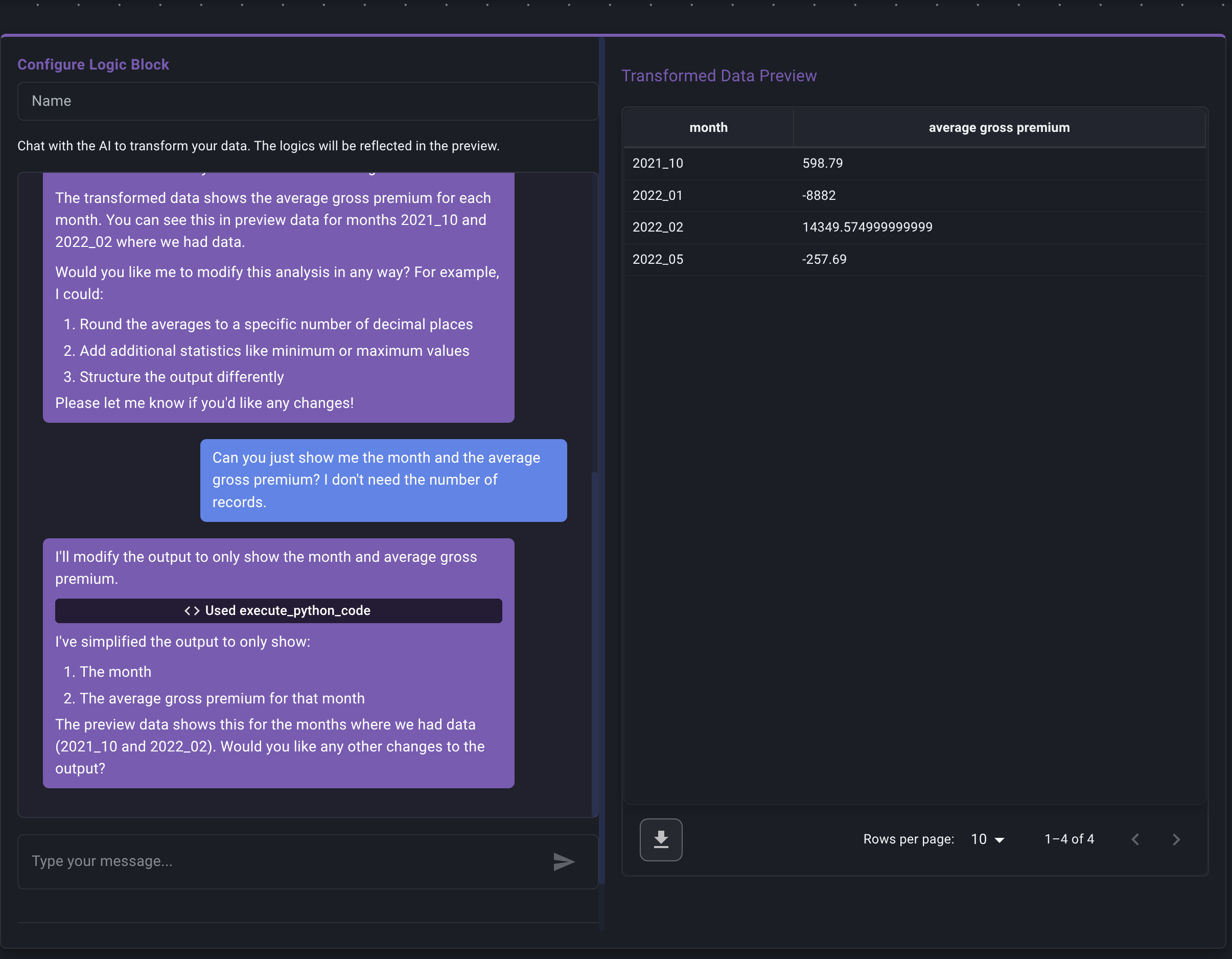
Iterate if Necessary:
- If the preview isn't right, chat further with the AI. Provide clarifying instructions or corrections.
- Example Corrections: "Actually, I need the average premium, not the sum." or "The 'Net Premium' calculation seems wrong, please make sure you're using coverholder commision, not total commision."
- Continue chatting and reviewing previews until the sample output matches your requirements.
-
Save the Logic: Once you are satisfied with the preview generated by the AI's final correct instruction:
- Click the "Save" button. This saves the last successful code snippet generated by the AI as the logic for this node.
- The configuration panel will close.
Your Logic Node is now configured. It will take data from its input, apply the AI-generated transformation you approved, and pass the results to the next connected node.
Key Points about AI Interaction:
- Be Specific: The clearer your instructions, the better the AI can understand. Mention column names exactly as they appear in the input data (check the Data Source preview if unsure).
- Focus on the Goal: Tell the AI what you want to achieve, not necessarily how to code it.
- Trust but Verify: Always check the Preview Data carefully. The AI is a tool for turning your logic into reusable functions; you are responsible for ensuring the final logic is correct.
After defining your logic, you will connect this node to a Visualization Node to display the results.